Weakly Supervised Methods and Medical Imaging

Our MICCAI work on weakly supervised lung disease detection recently posted to arxiv https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.15778. It treats a serious problem in weakly supervised medical object detection where not enough info is available using only the scene level labels. Our approach utilizes natural language information in large datasets with paired clinical reports and chest X-rays.
In order to bring referring expressions visual grounding advances to bear, we worked with an NIH radiologist to label clinically relevant objects in pneumonia and pneumothorax (collapsed lung) cases. Understanding a clinical chest xray is a complex task. The link here just scratches the surface on the factors radiologists infer: https://radiologyassistant.nl/chest/chest-x-ray/lung-disease.
Previous methods have focused on just the weakly supervised problem, but that has been called into question by the latest CVPR 2020 article https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.07437. There simply isn’t enough information.
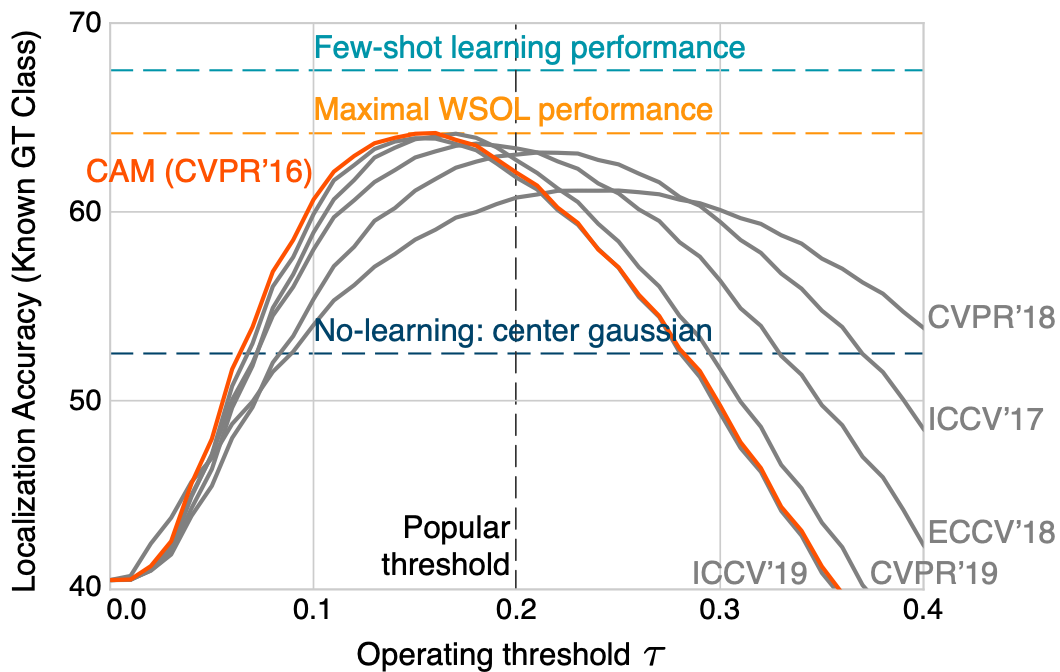 Choe, J. et. al. calling shennanigans on 5 methods using Class Activation Mapping (CAM). The five methods include data augmentation dropout, adversarial learning, pseudo-labeling, attention dropout, cutmix data augmentation.
Choe, J. et. al. calling shennanigans on 5 methods using Class Activation Mapping (CAM). The five methods include data augmentation dropout, adversarial learning, pseudo-labeling, attention dropout, cutmix data augmentation.
The excellent folks at MIT and Beth Israel have put together an amazing resource of chest xrays and clinical reports https://physionet.org/content/mimic-cxr-jpg/2.0.0/. We leveraged that to add referring expressions, both expertly annotated by our radiologist and automatically parsed using Stanford coreNLP parser.
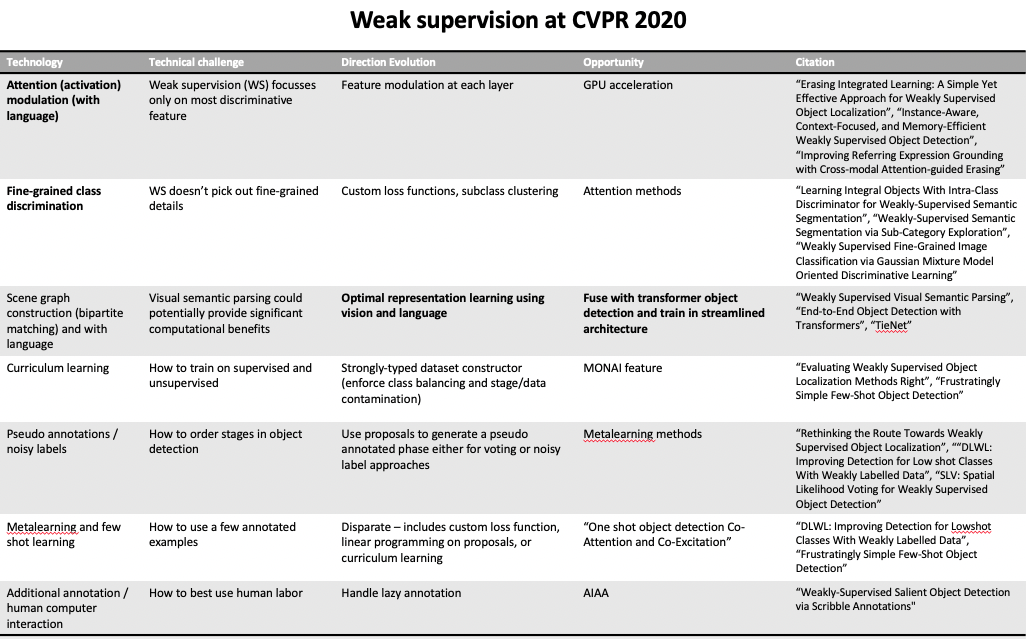 We analyzed the findings on weak supervision from CVPR and concluded that natural language methods formed an intuitive information channel. Large datasets with associated clinical reports are repositories of expert knowledge. We targeted aspects in bold with natural language information.
We analyzed the findings on weak supervision from CVPR and concluded that natural language methods formed an intuitive information channel. Large datasets with associated clinical reports are repositories of expert knowledge. We targeted aspects in bold with natural language information.
Using referring expressions and a combined one-stage vision-language detection architecture, we were able to show improvements over strong weakly supervised baselines, grad CAM which https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.07437 says are at SOTA.
The architecture and method form a valuable tool to unlock vast stores of data already collected by hospitals and Institutes. It’s a promising direction that is parallel to the recommendations from Choe, J. et. al. We release our annotations publicly here: https://github.com/leotam/MIMIC-CXR-annotations
@inproceedings{tamliterati2020,
author = {Tam, L.K., Wang, X., Turkbey, E., Lu, K., Wen, Y., Xu, D.},
title = {Weakly supervised one-stage vision and language disease detection using large scale pneumonia and pneumothorax studies},
booktitle={Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention -- MICCAI 2020},
year = {2020},
month = {March},
location = {NVIDIA, Santa Clara, CA, USA},
howpublished = {MICCAI 2020},
}
Additional reading: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.06666